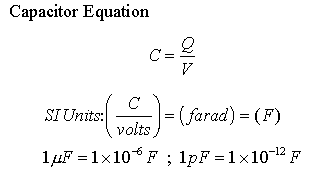Basic Electronics:
Principles of Electronics:
Ohm's Law:
All electronics equipment works on a fundamental physics principle known as Ohm's law, which states that a circuit contains a voltage directly proportional to the current and resistance encountered by the current in that circuit. The circuit comprises the electronic components also known as circuit elements, linked with wires to a battery and designed to obey Ohm's law.
Ohm:
- The practical unit of resistance is the ohm designated by the Greek letter omega: Ω
- A resistor is an electronic component designed specifically to provide resistance.
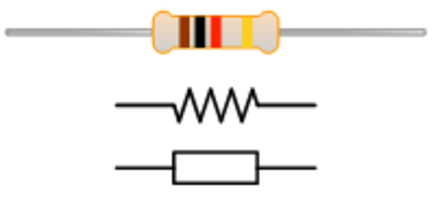
Resistor:
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
(or)
Resistor is an electrical component that reduces the electric current.
The resistor's ability to reduce the current is called resistance and is measured in units of ohms (symbol: Ω).
(or)

A device used to control current in an electric circuit by providing resistance.
Types of Resistors:
Color Coding in Resistor:
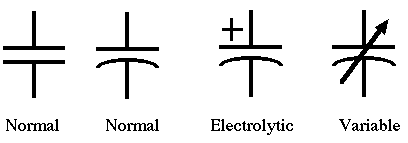
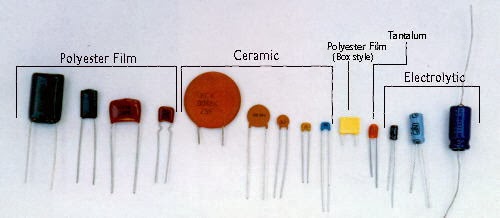
Capacitor:
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy electro-statically in an electric field.
(or)
An electric circuit element used to store charge temporarily, consisting in general of two metallic plates separated and insulated from each other by a dielectric.
(or)
A device used to store charge in an electrical circuit. A capacitor functions much like a battery, but charges and discharges much more efficiently (batteries, though, can store much more charge).
Types of Capacitors:
Inductor:
An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil.
(or)
An inductor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. In its simplest form, an inductor consists of a wire loop or coil. The inductance is directly proportional to the number of turns in the coil.